Build software encompasses the intricate process of creating innovative solutions that drive industries forward, from initial planning to final deployment. Dive into the world of software development as we explore the key stages and best practices that shape this dynamic field.
Introduction to Building Software
Building software refers to the process of creating computer programs and applications through coding, testing, and debugging. It involves designing solutions to specific problems or needs using technology.
Developing software is crucial for various industries as it helps streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance productivity. It enables businesses to automate tasks, analyze data, and deliver better services to customers.
Examples of Popular Software Products and Their Impact on Society
- Microsoft Office: Microsoft Office is a suite of productivity software that includes programs like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint. It has revolutionized the way people create documents, analyze data, and make presentations in both professional and personal settings.
- Adobe Photoshop: Adobe Photoshop is a graphic design software widely used for photo editing, digital art, and graphic design. It has transformed the visual communication industry and enabled artists and designers to unleash their creativity.
- Facebook: Facebook is a social networking platform that connects billions of people worldwide. It has changed the way people communicate, share information, and stay connected with friends and family.
Planning and Designing Software

Planning and designing software is a crucial phase in the development process, as it sets the foundation for the entire project. It involves mapping out the project scope, requirements, and overall structure before moving on to the implementation stage.
Creating detailed design documents before coding is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it helps in clarifying the project requirements and objectives, ensuring that all stakeholders are on the same page. Additionally, it serves as a roadmap for developers, guiding them on how to approach the coding phase. Detailed design documents also aid in identifying potential issues early on, preventing costly changes later in the development process.
Initial Steps in Planning a Software Project
- Define project scope and objectives.
- Gather requirements from stakeholders.
- Conduct feasibility studies to assess if the project is viable.
- Create a project plan outlining timelines, resources, and milestones.
Significance of User-Friendly Interfaces
Designing user-friendly interfaces is crucial for ensuring that the software is intuitive and easy to use for end-users. Some strategies for designing user-friendly interfaces include:
- Keep the interface simple and uncluttered.
- Use consistent design elements throughout the software.
- Provide clear navigation paths for users to easily access different features.
- Conduct usability testing to gather feedback and make improvements.
Coding and Development Process

In the software development process, coding and development play a crucial role in bringing the design and planning to life. This stage involves writing code, testing, debugging, and implementing the software.
Stages of the Software Development Life Cycle
- Requirement Analysis: Gathering and analyzing requirements from stakeholders.
- Design: Creating a high-level design and detailed design of the software.
- Implementation: Writing code based on the design specifications.
- Testing: Testing the software for bugs and issues.
- Deployment: Releasing the software for users.
- Maintenance: Regular updates and maintenance to ensure smooth operation.
Programming Languages in Software Development
- Java: A versatile language used for a wide range of applications.
- Python: Known for its simplicity and readability, widely used in data science and web development.
- C++: A powerful language often used in system programming and game development.
- JavaScript: Essential for web development and adding interactivity to websites.
Best Practices for Writing Clean and Efficient Code
- Use meaningful variable names and comments to improve readability.
- Follow coding standards and conventions to ensure consistency.
- Avoid redundant code and optimize algorithms for better performance.
- Regularly test and debug code to catch errors early in the development process.
Testing and Debugging: Build Software
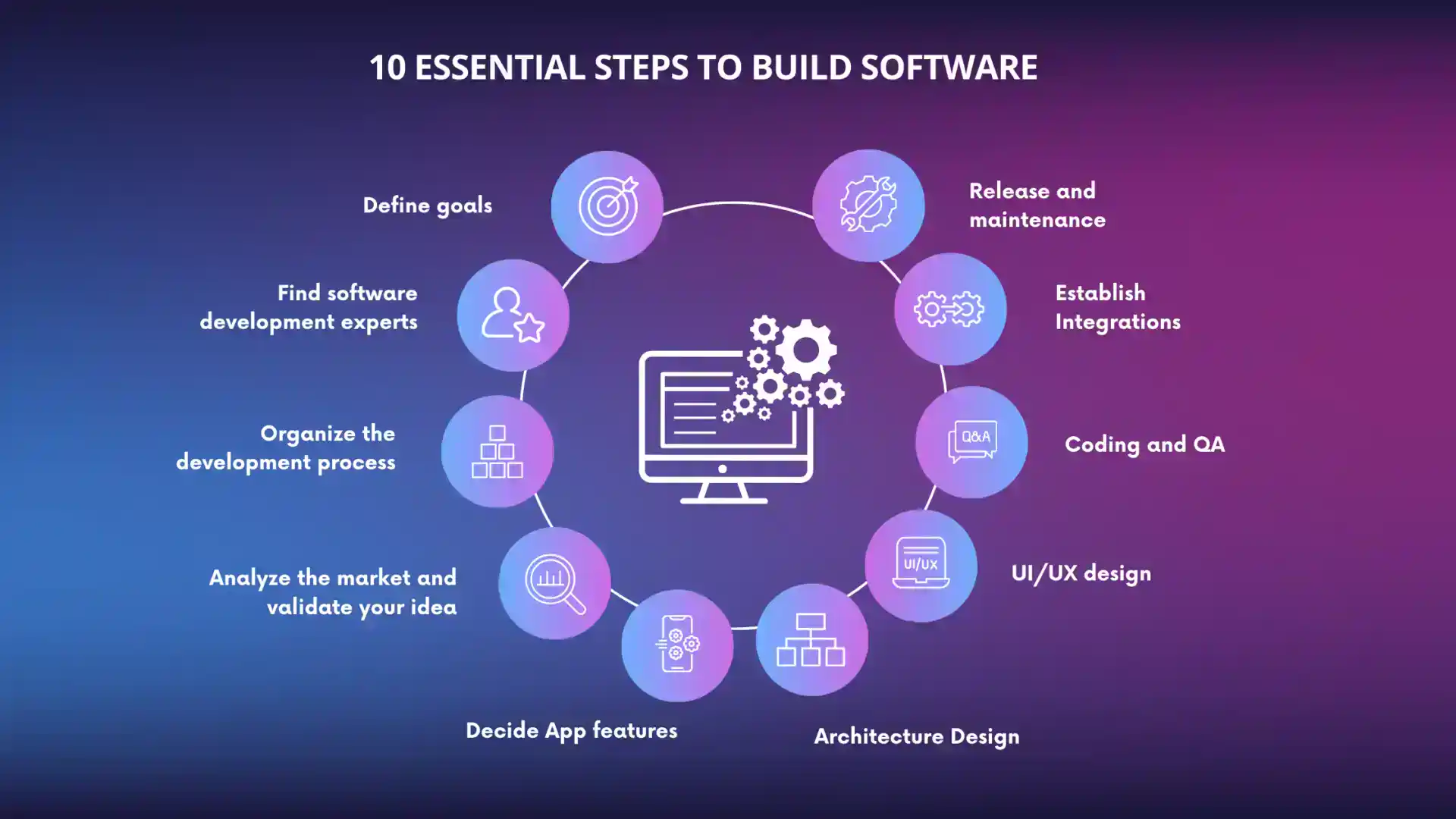
Software testing is a crucial step in the software development process as it helps ensure that the software functions as intended and meets the requirements of the end-users. Debugging, on the other hand, involves identifying and fixing errors or bugs in the code to improve the overall quality of the software.
Types of Testing Methodologies
- 1. Unit Testing: Involves testing individual units or components of the software in isolation.
- 2. Integration Testing: Focuses on testing how different modules work together.
- 3. System Testing: Tests the entire software system as a whole.
- 4. Acceptance Testing: Involves testing the software with end-users to ensure it meets their requirements.
Strategies for Identifying and Fixing Bugs
- 1. Use of Debugging Tools: Utilize tools like debuggers to identify and fix bugs in the code.
- 2. Code Reviews: Conduct thorough code reviews to catch any errors or bugs early in the development process.
- 3. Regression Testing: Perform regression testing to ensure that new code changes do not introduce new bugs.
- 4. Logging and Monitoring: Implement logging and monitoring mechanisms to track errors and issues in real-time.
Deployment and Maintenance
After the software has gone through the coding and testing phases, the next crucial step is deploying it to production environments. This process involves releasing the software to live servers where end-users can access and utilize it.
Regular maintenance and updates are essential for the longevity and effectiveness of the software. This includes fixing bugs, adding new features, improving performance, and addressing security vulnerabilities. Neglecting maintenance can lead to software becoming outdated, unreliable, and susceptible to security breaches.
Importance of Deployment Process
- Ensure thorough testing before deployment to avoid issues in production.
- Backup data and have a rollback plan in case of deployment failures.
- Communicate with stakeholders about the deployment schedule and any potential downtime.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
- Keep the software up-to-date with the latest technological advancements and security patches.
- Regular maintenance enhances performance, user experience, and overall software reliability.
- Proactive maintenance can prevent costly downtime and system failures.
Providing Customer Support and Issue Resolution, Build software
- Establish clear channels for customer support, such as a helpdesk, email, or live chat.
- Provide comprehensive documentation and FAQs to assist users in troubleshooting common issues.
- Implement a ticketing system to track and prioritize customer issues for timely resolution.
Conclusive Thoughts
Embark on your software development journey equipped with insights on planning, designing, coding, testing, and maintaining software to ensure lasting success in the digital landscape. Stay tuned for more exciting updates in the realm of software innovation.
